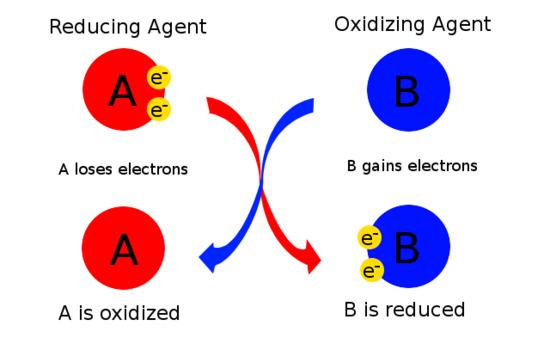
How to Tell Which Is the Best Reducing Agent
Lithium is therefore the most powerful reducing agent. The half reaction would be Li Li 1 e Oxidation of a Positive Oxidation State into a Higher Positive Oxidation State H 2 C 2 O 4 is also a good reducing agent.
8 2 Oxidizing And Reducing Agents Chemistry Libretexts
Good reducing agents include the active metals such as sodium magnesium aluminum and zinc which have relatively small ionization energies and low electro-negativities.
. Due to the smallest standard reduction potential lithium is the strongest reduction agent. It is allowing chlorine to be reduced by supplying these two electrons. The bigger the number the stronger the reducing.
At top end of electrochemical series there is lithium which is the strongest reducing agent and at the bottom end of electrochemical series there is fluorine which is the weakest reducing agent or. That allows sodium to be oxidized so chlorine is the agent for the oxidation of sodium or the oxidizing agent. Both of the half-cell reaction for Au are higher than the half-cell reaction of all the other element so I think use either one to compare is okay.
1 mL of BME Sigma 500 mL70 14 centsmL can make 29L of a 5 mM solution. B Nitrogen is being oxidized from an oxidation state of 0 to 1 so it is the reducing agent. This is determined by comparing the oxidation numbers of nitrogen.
You just need to arrange it so that the most negative one is the strongest reducing agent. Surely its lower down than lithium more like francium. The unpaired electron of francium is significantly less attracted to its nucleus due to electron shielding by.
By convention reduction potential or the propensity to be diminished are the normal electrode potentials. This eliminates choice B. Species that lie below ceH2 are stronger oxidizing agents.
What is the weakest reducing agent. Look on the RIGHT side to find substances that are going to be oxidized. Its most negative so its the most readily oxidised thus strongest reducing agent.
Heres a typical table of standard reduction potentials. And chlorine by undergoing reduction is taking the electrons from the 2 sodium atoms. Hydrogen is being oxidized from an oxidation state of 0 to 1 so it is the reducing agent.
Most positive E--most negative E weak reducing agen--strong reducing agent. Because N O 3 has the highest oxidation number of 5 compared to the other molecules it will most likely be the oxidizing agent. The oxidation state of the C atom is 3.
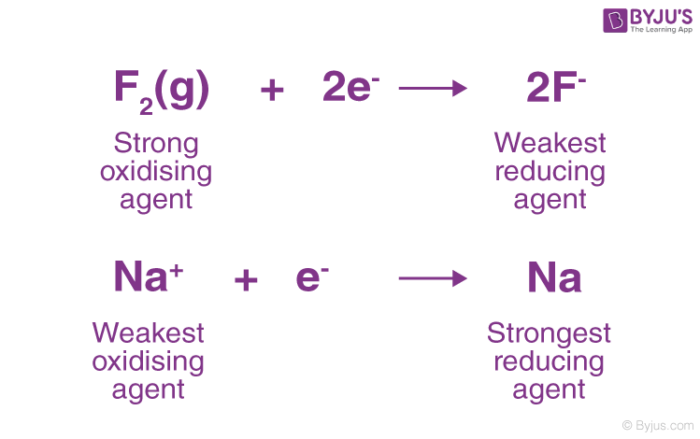
The best reducing agent is the compound that is most favorably oxidized. The strongest oxidizing agent in the list is F2 followed by H2O2 and so on down to the weakest oxidizing agent Li. The standard reduction potentials can be interpreted as a ranking of substances according to their oxidizing and reducing power.
Corrosion requires an anode and cathode to take place. While if we move downwards from hydrogen then the strength of reducing agents increases. It decreases another substance when something is oxidized becoming a reduction agent.
Lithium Li is a strong reducing agent because it readily loses an electron obtaining a 1 oxidation state. Valences computer alkali metal structure is ns1. Let me go ahead and write that in red here.
Dont quote me though. Is electronegativity the factor that determines the strength of reducing agents and oxidizing agents. As we move upwards from hydrogen in the electrochemical series then the strength of reducing agents decreases.
Metal hydrides such as NaH CaH 2 and LiAlH 4 which formally contain the H-ion are also good reducing agents. A reducing agent is a substance that causes another substance to reduce. We can know the strength of reducing agents by electrochemical series as well.
Are weak reducing agents. It has plenty of examples and practice problems for you. So to identify an oxidizing agent simply look at the oxidation number of an atom before and after the reaction.
I believe its Lithium - because of its standard electrode potential. This video tutorial shows you how to identify the oxidizing and reducing agent in a redox reaction. A Nitrogen is being reduced from an oxidation state of 0 to -3 so it is the oxidizing agent.
N H 3 is most likely to be a strong reducing agent. 4 gr of TCEP Pierce 10 gr356 35gr can make 29L of a 5 mM solution. Fluorine chlorine iron etc.
Since Li is easy to oxidize it is an excellent reducing agent it reduces something else when it is oxidized. If the oxidation number is greater in the product then it lost electrons and the substance was oxidized. Good reducing agents tend to consist of atoms with a low electronegativity the ability of an atom or molecule to attract bonding electrons and species with relatively small ionization energies serve as good reducing agents.
8 The best reducing agents are located at the bottom left of the periodic table low electronegativity and the best oxidizing agents are located at the top right of the periodic table high electronegativity excluding noble gases. Click to see full answer. Species in Table PageIndex1 that lie above H 2 are stronger reducing agents more easily oxidized than H 2.
Which metal is the strongest reducing agent The best reducing metal is lithium with the maximum negative value of electrode potential. The highest oxidizing agent is the weakest reducing agent. To tell which is the strongest reducing agent one can change the sign of its respective reduction potential to make it oxidation potential.
Look on the LEFT side of the half-reactions for substances that are going to be reduced. According to the table Mg2 aq is an oxidizing agent because it has no electrons to lose and can gain two electrons to form the neutral metal.

Inorganic Chemistry Best Oxidizing And Reducing Agents Na Zn 2 Ba Ba 2 And Ag Chemistry Stack Exchange

0 Response to "How to Tell Which Is the Best Reducing Agent"
Post a Comment